
Users may use this formula to find the probability of x-variate range, use the calculator to verify the results or generate the complete work with steps for normal distribution worksheet problems. The below formula is the mathematical representation of Gaussian distribution to know what are all the input parameters are being used to find the probability of area of data range in left, right or two tailed normal distributions. By using this normal distribution table & calculator, user may estimate what is the probability of standard normal variate range in left, right or two tailed normal distributions. The formula for calculating standard normal variable: z (x ). The negative z-score lies on left side represents the left tail & the positive score lies on right side represents right tail of the normal or Z-distribution. The negative & positive values of Z-score lies on the left & right side of the mean of standard normal distribution respectively. A smaller & larger standard deviation values represent how the data is tightly or loosely bundled around the mean accordingly. μ - σ & μ + σ represents the left and/or right side attributes of distribution. One of the most basic skills needed for the CRE exam is the ability to correctly read the Standard Normal Table. The range of data or standard normal variate x lies anywhere between -∞ and +∞.
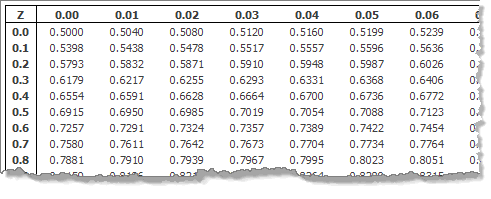
Related Calculators What Is A Z Score Table Simply put, a z. Generally, 68.27%, 95.45% and 99.73% data observations fall around the mean between ☑σ, ☒σ and ☓σ respectively. Use this Z score table to find an area between the mean and Z score standard deviation. By using this normal distribution table & calculator, user may estimate what is the probability of standard normal variate range in left, right or two tailed normal distributions.

Negative Z Score Table: It means that the observed value is below the mean. The negative z-score lies on left side represents the left tail & the positive score lies on right side represents right tail of the normal or Z-distribution. The data around the mean generally looks similar to the bell shaped curve having left & right asymptote tails both extends to infinity. A standard normal table (also called the unit normal table or z-score table). It's a continuous probability density function used to find the probability of area of standard normal variate X such as P(X X1), P(X X2) or P(X1 < X < X2) in left, right or two tailed normal distributions. Normal Distribution is also well known by Gaussian distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
